Superordinate goals ap psychology definition – In AP Psychology, superordinate goals hold immense significance in shaping human behavior and well-being. These long-term, overarching aspirations guide and motivate individuals, influencing their actions and life choices. This comprehensive exploration delves into the definition, types, formation, and impact of superordinate goals, providing a deeper understanding of their role in psychological functioning.
Superordinate goals encompass a wide range of aspirations, from personal growth and fulfillment to societal contributions. They often transcend immediate gratification, fostering a sense of purpose and direction in life. Their influence extends beyond individual well-being, impacting relationships, communities, and even global affairs.
1. Definition of Superordinate Goals in AP Psychology: Superordinate Goals Ap Psychology Definition
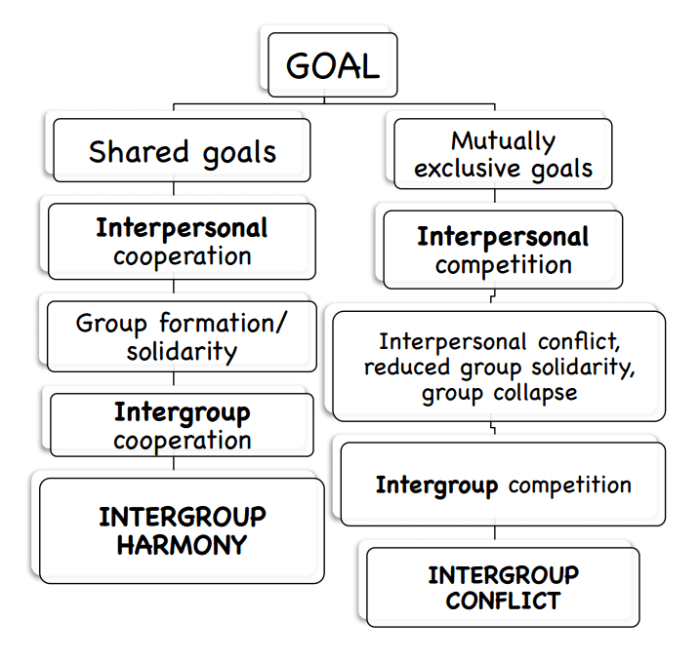
Superordinate goals are overarching, long-term goals that provide direction and meaning to an individual’s life. They are often abstract and aspirational, transcending specific tasks or accomplishments.
Superordinate goals are significant because they:
- Provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment
- Motivate and guide behavior
- Shape an individual’s values and priorities
Examples of superordinate goals include:
- Becoming a successful doctor
- Raising a happy and healthy family
- Making a positive impact on the world
2. Types of Superordinate Goals

2.1 Content and Scope, Superordinate goals ap psychology definition
Superordinate goals can be classified based on their content and scope:
- Personal goals:Focus on individual growth and well-being
- Social goals:Aim to benefit others or society as a whole
- Transcendental goals:Connect individuals to something larger than themselves (e.g., spirituality, nature)
2.2 Intrinsic and Extrinsic Goals
Superordinate goals can also be categorized as intrinsic or extrinsic:
- Intrinsic goals:Driven by internal rewards (e.g., personal satisfaction, accomplishment)
- Extrinsic goals:Motivated by external rewards (e.g., money, status, recognition)
Personal values and beliefs play a significant role in shaping the formation of superordinate goals.
3. Formation and Development of Superordinate Goals
The formation and development of superordinate goals are influenced by various factors:
- Social learning:Observing and imitating others who pursue meaningful goals
- Cultural influences:Cultural norms and values shape aspirations and goals
- Individual experiences:Life events, successes, and challenges can shape an individual’s superordinate goals
Goal setting is a process that involves:
- Identifying desired outcomes
- Developing strategies to achieve those outcomes
- Monitoring progress and making adjustments as needed
4. Measurement and Assessment of Superordinate Goals
Measuring and assessing superordinate goals is challenging due to their abstract nature.
- Self-report measures:Questionnaires and interviews allow individuals to report on their goals
- Observational methods:Observing behavior and actions related to goals
- Goal-directed activities:Analyzing activities that align with stated goals
Each assessment tool has strengths and limitations, and researchers often combine multiple methods to obtain a comprehensive understanding of superordinate goals.
5. Superordinate Goals and Well-being
Superordinate goals have a significant impact on subjective well-being:
- Positive relationship:Pursuing meaningful goals enhances life satisfaction, happiness, and mental health
- Buffering effect:Superordinate goals can protect individuals from negative life events and promote resilience
- Coping mechanisms:Goals provide a sense of direction and purpose during challenging times
6. Superordinate Goals in Therapy and Counseling

Superordinate goals play a vital role in therapeutic interventions:
- Identification and development:Therapists help clients identify and develop meaningful superordinate goals
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy:Superordinate goals provide a framework for changing negative thought patterns and behaviors
- Positive psychology:Interventions focus on fostering strengths and promoting well-being through the pursuit of meaningful goals
User Queries
What distinguishes superordinate goals from other types of goals?
Superordinate goals are characterized by their long-term nature, broad scope, and intrinsic motivation. They transcend specific tasks or immediate rewards, instead focusing on overarching life aspirations and values.
How do superordinate goals influence behavior?
Superordinate goals provide direction and purpose to behavior, motivating individuals to engage in actions that align with their long-term aspirations. They can enhance persistence, resilience, and overall well-being.
Can superordinate goals change over time?
Yes, superordinate goals can evolve and adapt as individuals grow and experience life changes. They may be influenced by social learning, cultural shifts, and personal reflections.