Which concrete building type of construction may be cast larger? This intriguing question delves into the realm of architectural engineering, where the boundaries of concrete’s capabilities are constantly tested. Concrete, a versatile and durable material, has revolutionized the construction industry, enabling the creation of towering skyscrapers, sprawling bridges, and other monumental structures.
However, understanding the factors that influence the maximum size of concrete castings is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and pushing the limits of architectural design.
As we explore the intricacies of concrete casting, we will uncover the key factors that determine the size of a concrete structure, delve into case studies of notable large concrete buildings, and examine the latest technological advancements that are expanding the possibilities for even larger and more ambitious concrete constructions.
Building Types and Sizes
Concrete buildings come in various types, each with its own typical size range. Common building types include residential structures, commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and public infrastructure. Residential buildings, such as houses and apartments, are typically smaller in size, with heights ranging from one to a few stories.
Commercial buildings, like offices and shopping malls, can be larger, with heights of up to several stories. Industrial facilities, such as warehouses and factories, often require large open spaces, resulting in larger building sizes. Public infrastructure, such as bridges and tunnels, can be of significant size, with complex structural designs.
The size of a concrete building can significantly impact its structural design and construction methods. Larger buildings require more robust structural systems to withstand increased loads and ensure stability. This may involve the use of thicker concrete sections, additional reinforcement, and more complex structural elements.
Additionally, larger buildings may require more complex construction methods, such as the use of formwork systems, cranes, and specialized equipment.
Factors Influencing Casting Size
The maximum size of a concrete building that can be cast is determined by several key factors:
Concrete Strength
The strength of concrete is a critical factor in determining casting size. Higher-strength concrete allows for thinner sections and larger spans, resulting in larger buildings. Advanced concrete mixes, such as high-performance concrete and self-compacting concrete, can further enhance casting size.
Reinforcement
Reinforcement plays a vital role in increasing the strength and load-bearing capacity of concrete. The type, amount, and distribution of reinforcement can significantly influence the maximum casting size. Steel reinforcement, in the form of rebars or meshes, is commonly used to reinforce concrete structures.
Formwork
Formwork is the temporary structure that shapes and supports the concrete during the casting process. The design and capacity of the formwork limit the size of the concrete pour. Advanced formwork systems, such as slip-form and jump-form systems, enable the casting of large concrete structures with complex shapes and geometries.
Case Studies of Large Concrete Buildings
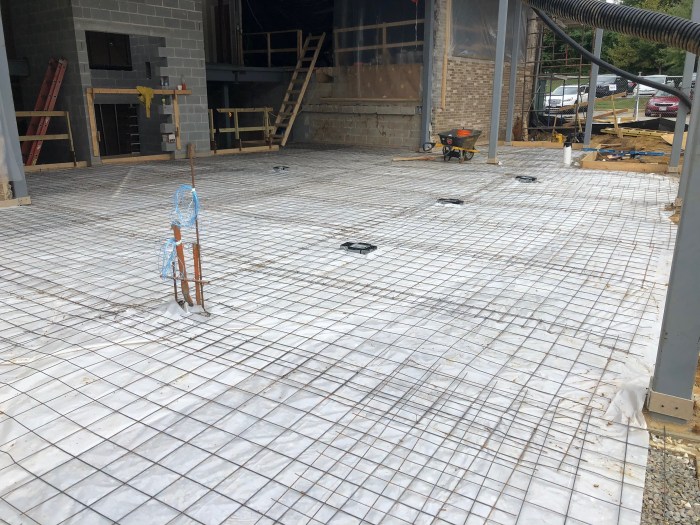

Several notable large concrete buildings have been constructed around the world, showcasing the capabilities and advancements in concrete casting:
Burj Khalifa, Dubai, Which concrete building type of construction may be cast larger
Standing at a height of 828 meters, Burj Khalifa is the tallest building in the world. Its concrete core structure was cast using high-strength concrete and advanced formwork systems, enabling the construction of this iconic skyscraper.
Three Gorges Dam, China
The Three Gorges Dam is one of the largest concrete structures ever built. The massive dam required the casting of millions of cubic meters of concrete, using specialized casting methods and concrete mixes designed for durability and longevity.
Design Considerations for Large Concrete Castings

Planning large concrete castings requires careful consideration of several design aspects:
Structural Analysis
Thorough structural analysis is essential to ensure the stability and integrity of large concrete structures. Engineers must consider factors such as dead loads, live loads, wind loads, and seismic forces.
Load Distribution
The distribution of loads is critical in large concrete castings. Structural elements, such as beams, columns, and slabs, must be designed to transfer loads efficiently to the foundation.
Joint Design
Joints between concrete elements play a vital role in the overall performance of large structures. Joints must be designed to accommodate movement, expansion, and contraction, while maintaining structural integrity.
Technological Advancements in Concrete Casting
Technological advancements have significantly expanded the possibilities for large concrete castings:
High-Performance Concrete
High-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior strength, durability, and workability, allowing for thinner sections and larger spans in concrete structures.
Self-Compacting Concrete
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) flows easily into formwork, reducing the need for vibration and improving casting efficiency. SCC is particularly suitable for complex shapes and congested reinforcement.
Advanced Formwork Systems
Advanced formwork systems, such as slip-form and jump-form systems, enable continuous casting of large concrete structures. These systems improve construction speed and efficiency.
FAQ: Which Concrete Building Type Of Construction May Be Cast Larger
What factors influence the maximum size of a concrete building that can be cast?
The maximum size of a concrete building that can be cast is influenced by several factors, including concrete strength, reinforcement, formwork, and structural design.
What are some notable examples of large concrete buildings?
Notable examples of large concrete buildings include the Burj Khalifa, the Hoover Dam, and the Sydney Opera House.
How have technological advancements impacted concrete casting?
Technological advancements such as self-compacting concrete, high-performance concrete, and 3D printing have expanded the possibilities for large concrete castings by improving concrete strength, workability, and casting efficiency.