One manifestation of the patient’s illness was sweating or, medically known as diaphoresis, is a common symptom that can indicate a variety of underlying medical conditions. Excessive sweating can be a sign of infection, hormonal imbalances, or neurological disorders, and it can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of sweating as a manifestation of illness, providing healthcare professionals with the necessary knowledge to effectively manage this condition in their patients.
Causes of Sweating
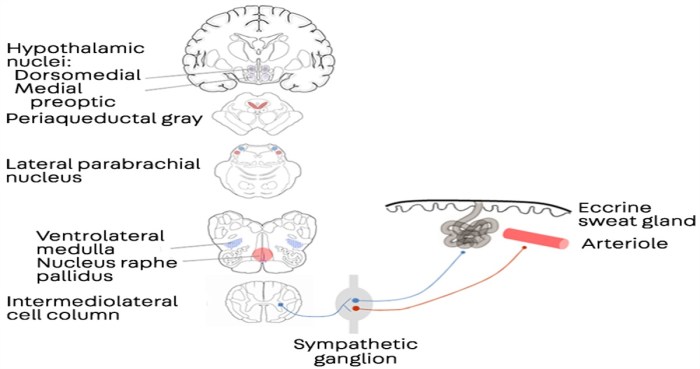
Sweating, or diaphoresis, is a natural physiological response to various stimuli, including heat, exercise, and emotional stress. However, excessive sweating, known as hyperhidrosis, can be a manifestation of underlying medical conditions.
Potential causes of sweating as a manifestation of illness include:
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can cause fever and chills, leading to sweating.
- Endocrine disorders: Hyperthyroidism, diabetes, and pheochromocytoma can disrupt hormone regulation, resulting in excessive sweating.
- Neurological disorders: Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and autonomic dysreflexia can affect the nervous system’s control of sweating.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and anticholinergics, can cause sweating as a side effect.
- Malignancies: Some types of cancer, such as lymphoma and leukemia, can cause fever and night sweats.
The physiological mechanism involved in sweating as a response to illness is complex and involves the activation of the sympathetic nervous system and the release of hormones such as adrenaline and acetylcholine. These substances stimulate the sweat glands to produce sweat, which evaporates from the skin’s surface, cooling the body.
Diagnosis of Sweating: One Manifestation Of The Patient’s Illness Was Sweating Or
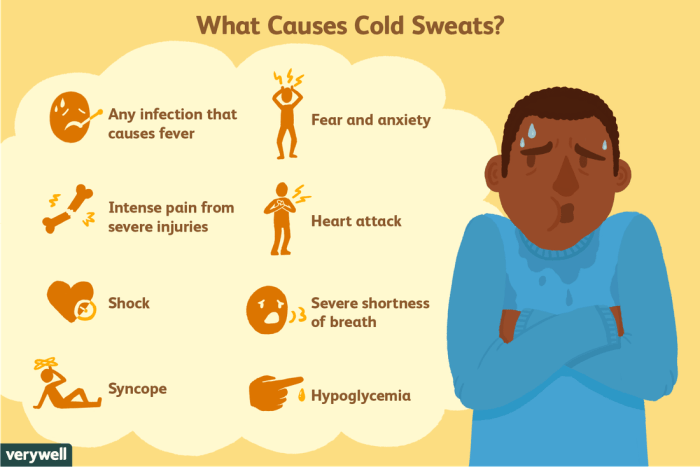
Diagnosing sweating as a manifestation of illness involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and physical examination.
Physical examination includes assessing the patient’s skin for excessive moisture, examining for signs of infection or other underlying conditions, and measuring vital signs such as temperature and blood pressure.
Medical history should include information about the patient’s symptoms, duration of sweating, associated factors, and any medications or recent illnesses.
Laboratory tests may be ordered to rule out underlying medical conditions, such as blood tests for infections or thyroid function tests.
Differential diagnosis is crucial to distinguish between primary hyperhidrosis, which is a localized condition without an underlying cause, and secondary hyperhidrosis, which is a manifestation of another medical condition.
Treatment of Sweating

Treatment for sweating as a manifestation of illness focuses on managing the underlying cause.
Pharmacological interventions may include:
- Anticholinergics: These medications block the action of acetylcholine, reducing sweat production.
- Botox injections: Botulinum toxin injections can temporarily paralyze sweat glands, reducing sweating.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants can have anticholinergic effects, reducing sweating.
Non-pharmacological interventions include:
- Iontophoresis: This procedure uses electrical currents to block sweat glands.
- Microwave thermolysis: This treatment uses microwave energy to destroy sweat glands.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding triggers such as heat, caffeine, and alcohol can help reduce sweating.
Nursing Considerations

Nurses play a vital role in caring for patients with sweating as a manifestation of illness.
Nursing interventions include:
- Patient education and support: Educating patients about the causes and management of sweating can empower them to manage their symptoms.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Nurses monitor patients’ symptoms, response to treatment, and overall well-being.
- Collaboration with healthcare team: Nurses collaborate with physicians and other healthcare professionals to develop and implement a comprehensive treatment plan.
Common Queries
What are the most common causes of sweating as a manifestation of illness?
The most common causes include infections, hormonal imbalances, neurological disorders, and certain medications.
How is sweating as a manifestation of illness diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests to identify the underlying cause.
What are the treatment options for sweating as a manifestation of illness?
Treatment options include pharmacological interventions (e.g., anticholinergics), non-pharmacological interventions (e.g., lifestyle modifications), and targeted therapy based on the underlying cause.